Buy Remicade (infliximab) 100 mg 1 vial Online For Sale
$385.00
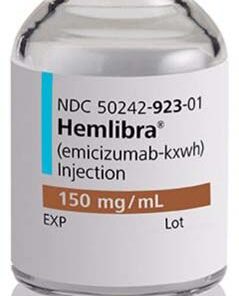
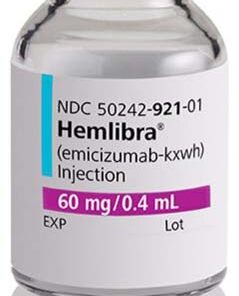
Remicade (infliximab) is an anti-TNF-alpha antibody medication used for the treatment of various autoimmune disorders, including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and ankylosing spondylitis. The drug is administered through an intravenous infusion, and the dosages are determined by the patient’s condition, weight, age, and overall health. Remicade has been shown to be effective in clinical trials, but it may cause side effects such as infusion reactions, infections, blood disorders, congestive heart failure, and the formation of antibodies. Patients receiving Remicade should be closely monitored for any signs of infections or side effects, and healthcare providers should carefully evaluate possible risks and benefits of the medication.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.