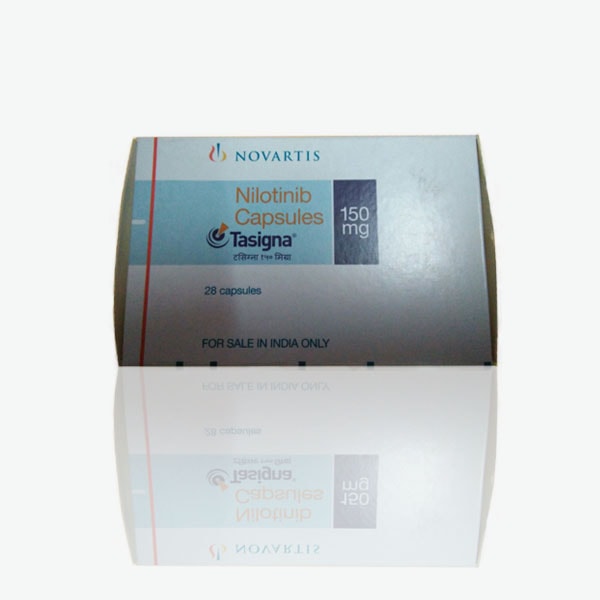
Buy Tasigna : Nilotinib 150 Mg Capsules Online
$171.24
Brand Name: Tasigna
Generic Name: Nilotinib
Manufacturer: Roche Holding AG
Strength: 150 mg
Dosage Form: Capsules
Packaging: Pack of 28 Capsules
Prescription Required *
Tasigna is a medication indicated for the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). It is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that blocks the activity of BCR-ABL, the abnormal protein that is responsible for the growth and survival of CML cells.
Composition:
Tasigna capsules contain nilotinib as the active ingredient.
Uses:
Tasigna is used to treat adults with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) chronic phase chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). It is also indicated for the treatment of chronic phase and accelerated phase Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) CML in adults who are resistant or intolerant to prior therapy including imatinib.
Usage and Dosage:
Tasigna capsules should be taken orally twice daily, with food. The recommended starting dose of Tasigna for newly diagnosed CML patients is 300 mg administered twice daily. The recommended dose for patients with chronic or accelerated phase CML who are resistant or intolerant to prior therapy including imatinib is 400 mg administered twice daily.
Storage Conditions:
Tasigna capsules should be stored at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C-30°C (59°F-86°F). Keep the capsules in their original container and protect from light.
Mechanism of Action:
Tasigna is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that binds to the ATP-binding site of BCR-ABL, causing inhibition of the abnormal protein’s activity. Tasigna blocks the pathway that signals the growth of cancer cells in patients with CML.
Contraindications:
Tasigna is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to nilotinib or to any of its ingredients. It is also contraindicated in patients with hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, or long QT syndrome. Tasigna should not be used during pregnancy or lactation.
Interactions:
Tasigna is metabolized primarily in the liver by the CYP3A4 enzyme. Drugs that interact with CYP3A4, such as ketoconazole, erythromycin, and grapefruit juice, may increase the exposure to Tasigna and increase the risk of adverse reactions. Substances that may decrease the exposure to Tasigna include drugs that induce CYP3A4, such as rifampin and St. John’s Wort.
Side Effects:
The most common side effects associated with Tasigna include nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, rash, itching, headache, constipation, vomiting, abdominal pain, joint pain, infection, and muscle pain. Serious side effects that require immediate medical attention include severe bleeding, liver problems, low blood counts, QT prolongation, pancreatitis, and tumor lysis syndrome.
In conclusion, Tasigna is an effective and targeted therapy for chronic myelogenous leukemia. Patients should be closely monitored for any adverse reactions and should follow their physician’s instructions regarding dosage and administration.
Be the first to review “Buy Tasigna : Nilotinib 150 Mg Capsules Online” Cancel reply
Related products
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.