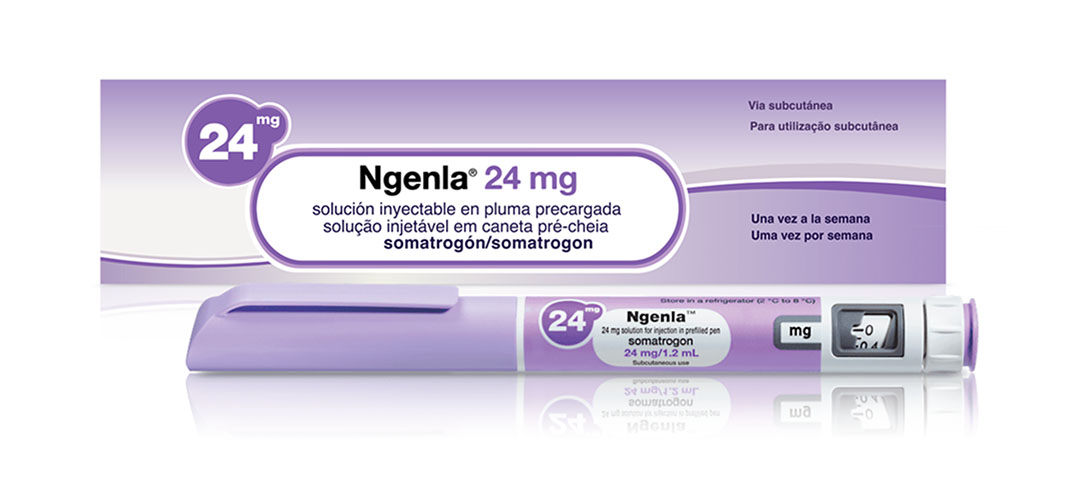
Buy Ngenla (somatrogon-ghla) Injection 24MG/72IU for Pediatric GHD (pGHD)
From $999.00
Ngenla® (somatrogon-ghla) is a long-acting, recombinant human growth hormone analog designed to treat pediatric patients with growth hormone deficiency (pGHD). Developed for once-weekly subcutaneous administration, Ngenla® provides an innovative alternative to daily growth hormone therapies, helping to simplify treatment routines and support better adherence.
Overview
Ngenla (somatrogon-ghla) is a cutting-edge, once-weekly, long-acting recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) designed to treat pediatric patients with growth hormone deficiency (pGHD). Developed through advanced protein engineering, Ngenla offers an innovative approach to hormone replacement therapy, aiming to optimize clinical outcomes while reducing the burden of daily injections associated with traditional growth hormone treatments. Its unique molecular design, superior pharmacokinetic profile, and established efficacy make Ngenla a transformative choice for healthcare providers and families seeking better management options for children with GHD.
Mechanism of Action
Ngenla is a modified form of somatropin, the naturally occurring human growth hormone. Through recombinant DNA technology, somatrogon-ghla is engineered by fusing a single copy of the C-terminal peptide (CTP) from the beta subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) to the amino acid sequence of somatropin. This strategic modification extends the circulating half-life of the molecule, allowing for once-weekly administration without compromising the biological activity of native growth hormone.
Upon administration, Ngenla binds to the growth hormone receptor (GHR) on target cells, activating the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. This stimulation results in the transcription of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), which is crucial for promoting skeletal growth, cell proliferation, and metabolic regulation. Elevated and sustained IGF-1 levels support normal growth patterns in children with GHD.
Indications and Usage
Ngenla is indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients aged 3 years and older who have growth failure due to inadequate secretion of endogenous growth hormone (pGHD). It serves as an essential therapeutic option for promoting growth, improving final adult height outcomes, and addressing psychosocial challenges related to short stature.
Clinical Efficacy
The efficacy of Ngenla was demonstrated in pivotal Phase 3 clinical trials involving treatment-naïve children diagnosed with pGHD. In a 12-month, randomized, open-label study, Ngenla was non-inferior to daily somatropin (Genotropin) in terms of annualized height velocity. Children treated with Ngenla achieved comparable growth outcomes with a more convenient once-weekly injection schedule.
Key findings from the trial include:
-
Significant improvement in annualized height velocity (AHV) at 52 weeks.
-
Maintenance of IGF-1 levels within age-appropriate normal ranges.
-
Favorable safety profile consistent with that observed for daily rhGH therapies.
-
High patient and caregiver satisfaction, attributed to reduced injection frequency.
Dosing and Administration
Ngenla is administered via subcutaneous injection once weekly. The recommended initial dosage is 0.66 mg/kg body weight, delivered once every seven days. The injection site should be rotated between the abdomen, thigh, upper arm, or buttocks to minimize the risk of lipodystrophy. Dosing adjustments may be necessary based on clinical response, IGF-1 serum concentrations, and tolerability.
Ngenla is supplied in a prefilled, ready-to-use, single-patient-use pen device, designed to facilitate precise dosing and ease of use for caregivers and healthcare professionals alike. Comprehensive training is provided to ensure proper administration techniques.
Safety Profile
The safety and tolerability of Ngenla are well-established, with adverse events generally mild to moderate in severity. Commonly reported side effects include:
-
Injection site reactions (e.g., redness, swelling, or pain)
-
Headache
-
Nausea
-
Arthralgia
-
Fatigue
Less commonly, patients may experience hypersensitivity reactions, glucose intolerance, or intracranial hypertension. As with all growth hormone therapies, the risk of neoplasia and slipped capital femoral epiphysis should be carefully monitored.
Patients should be regularly assessed for treatment-related adverse events, growth parameters, and IGF-1 levels to ensure optimal safety and efficacy outcomes.
Special Considerations
-
Contraindications: Ngenla is contraindicated in patients with acute critical illness following open heart surgery, abdominal surgery, multiple accidental trauma, or those with acute respiratory failure. It should also not be used in patients with active malignancy.
-
Warnings and Precautions: Monitor for signs of glucose intolerance, intracranial hypertension, scoliosis progression, and hypothyroidism during treatment. Growth hormone therapy may unmask previously undiagnosed central adrenal insufficiency.
-
Drug Interactions: Concomitant glucocorticoid therapy may inhibit the growth-promoting effects of somatrogon-ghla. Dose adjustments may be necessary when coadministered with glucocorticoids.
-
Pregnancy and Lactation: Ngenla is not indicated for use in pregnant or breastfeeding individuals. Although animal studies have not shown teratogenic effects, its safety in human pregnancy is not established.
Patient and Caregiver Support
Recognizing the emotional and practical challenges of managing pGHD, Pfizer offers comprehensive support programs alongside Ngenla therapy. These include:
-
Personalized injection training
-
24/7 nurse helpline
-
Financial assistance resources
-
Mobile apps for dose reminders and injection tracking
-
Educational materials to enhance understanding and adherence
Such programs aim to empower families, foster confidence, and promote long-term therapeutic success.
Storage and Handling
Ngenla pens should be stored refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and protected from light. Do not freeze. Before administration, the pen can be kept at room temperature (up to 25°C or 77°F) for up to 28 days. After this period, any unused product should be discarded.
Innovation and Future Directions
The development of Ngenla represents a major milestone in endocrine therapeutics, embodying the trend towards less burdensome, patient-centered treatments. Long-acting growth hormone analogs like Ngenla are anticipated to significantly improve adherence, quality of life, and overall health outcomes in pediatric populations. Ongoing studies are evaluating its potential use in additional indications, including adult growth hormone deficiency and other growth disorders.
Conclusion
Ngenla (somatrogon-ghla) offers an exceptional advancement in the management of pediatric growth hormone deficiency. Its once-weekly dosing, robust efficacy, and favorable safety profile distinguish it as a preferred option for clinicians and families seeking a more manageable and effective growth hormone therapy. With Ngenla, the journey towards healthier growth and a brighter future becomes a little easier — one weekly dose at a time.
| Quantity | 1 Pen(72IU), 2 Pens(144IU), 3 Pens(216IU) |
|---|






MomOnAMission78 –
My son is 5 and has been on Ngenla for four months now. He’s already showing more energy, better appetite, and is growing faster than we’ve ever seen. The injection process is smooth, and the device is super parent-friendly. We used to dread daily hormone shots—now it’s just part of our Sunday night routine. Can’t recommend it enough.
DrLeoPedsMD –
As a pediatric endocrinologist, I’ve found the 24MG dose of Ngenla ideal for younger children or those just starting GH therapy. The tolerability has been excellent, and parents love the convenience of once-weekly administration. Kids are growing, IGF-1 levels are staying stable, and overall compliance is much better than with daily regimens. This formulation makes introducing GH therapy far less intimidating.
HappyHeightsMama –
We started my 6-year-old on the 24MG dose of Ngenla a few months ago, and I’m already seeing steady growth progress. She was falling off the growth curve, but now she’s right back on track. The once-weekly injections are a huge relief compared to daily shots, and she barely notices them. So grateful we found a treatment that works without disrupting her daily life.