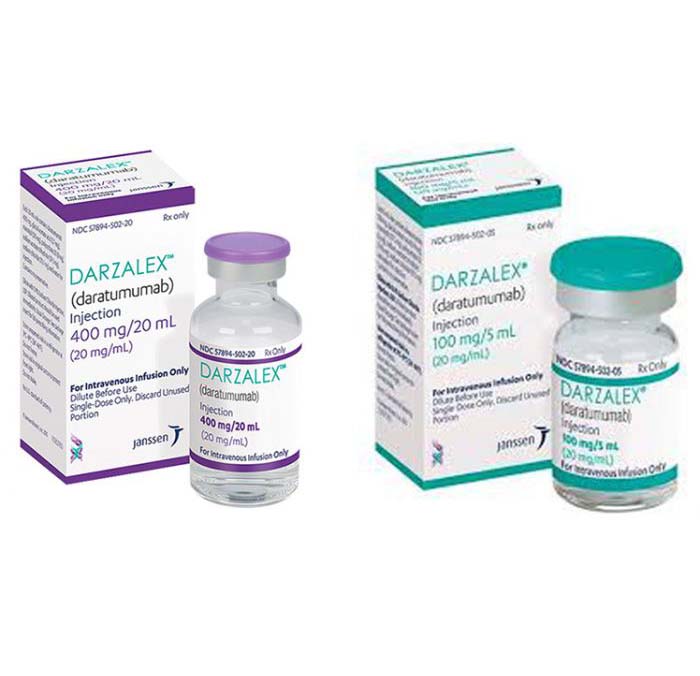
Buy Darzalex (daratumumab) Online For Sale
From $439.00
Disease Indications: Multiple Myeloma
Manufacturer: Janssen-Cilag International N.V.
Usage: Intravenous
Medicine approved by:
European Medical Agency (EMA)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
Health Canada
Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA)
Medsafe (NZ)
Darzalex (daratumumab) is a monoclonal antibody used to treat multiple myeloma by targeting the CD38 protein on myeloma cells. The drug is approved by the FDA and may be used alone or in combination with other medications.
Introduction
Darzalex (daratumumab) is a monoclonal antibody used to treat multiple myeloma, a type of blood cancer that affects plasma cells in the bone marrow. Darzalex is designed to target a protein called CD38, which is present on the surface of myeloma cells. By binding to CD38, Darzalex helps to destroy cancer cells and slow the progression of the disease.
Uses
Darzalex is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of multiple myeloma in several settings. The drug may be used alone or in combination with other medications, such as lenalidomide and dexamethasone, in patients who have received at least one previous therapy. Darzalex may also be used in combination with bortezomib, melphalan, and prednisone for the treatment of newly diagnosed multiple myeloma in patients who are not eligible for autologous stem cell transplant.
How It Works
Darzalex is a monoclonal antibody that targets CD38, a protein that is heavily expressed on the surface of myeloma cells. By binding to CD38, Darzalex depletes the number of myeloma cells and may also enhance the immune system’s ability to recognize and attack cancer cells. The drug is given intravenously and is typically administered over several hours.
Dosing
The recommended dose and schedule for Darzalex will vary depending on the specific treatment plan and other factors, such as the patient’s age and overall health. The drug is administered intravenously by a healthcare professional and may be given on a weekly or biweekly schedule, depending on the dosing regimen.
Side Effects
Darzalex can cause a range of side effects, which may vary in severity depending on the patient’s individual treatment and medical history. Some common side effects of Darzalex include infusion-related reactions, fatigue, nausea, and diarrhea. The drug can also cause more serious side effects, such as lung infections and low white blood cell counts. Patients should report any symptoms they experience to their healthcare provider immediately, as prompt medical attention can help manage potential side effects.
Drug Interactions
Darzalex may interact with other medications, including other cancer treatments and immunosuppressive drugs. Patients should notify their healthcare provider of all medications they are taking, including prescription, over-the-counter, herbal, and vitamin supplements, to avoid potential drug interactions.
Contraindications
Darzalex is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to the drug or any of its components. The drug may also not be recommended for use in patients with a history of severe infusion-related reactions or respiratory infections.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Darzalex may harm a developing fetus and should not be used during pregnancy unless the potential benefits outweigh the risks. Women of childbearing potential should use effective contraception during treatment and for at least three months after the last dose of Darzalex. It is unknown whether Darzalex is excreted in breast milk, and women should avoid breastfeeding while on this medication.
Conclusion
Darzalex (daratumumab) is a monoclonal antibody used to treat multiple myeloma, a type of blood cancer that affects plasma cells in the bone marrow. The drug targets the CD38 protein and helps to destroy cancer cells and slow the progression of the disease. Darzalex is typically given intravenously and may be used alone or in combination with other medications. Side effects of Darzalex can include infusion-related reactions, fatigue, and respiratory infections. The drug is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to its components and may not be recommended for use in certain patients. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid Darzalex unless the benefits outweigh the risks. Patients should discuss their specific treatment plan and potential risks and benefits of Darzalex with their healthcare provider.
| Package | 1 vial of 100 mg/5 mL, 1 vial of 400 mg/20 mL |
|---|
Be the first to review “Buy Darzalex (daratumumab) Online For Sale” Cancel reply
Related products
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.