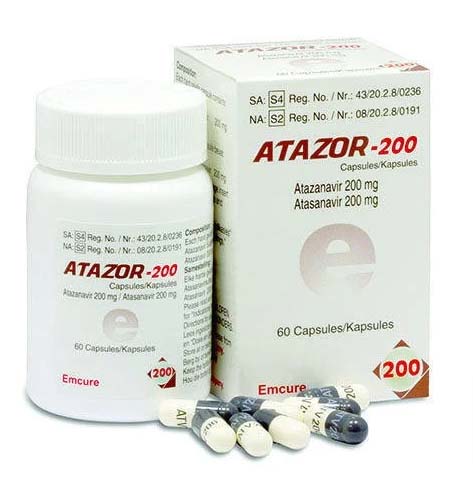
Buy Atazor : Atazanavir 200 mg Capsules Online Emcure Pharmaceuticals
$48.42
Brand Name : Atazor
Composition : Atazanavir
Manufacturer: Emcure Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
Strength : 200 mg
Form : Capsules
Packaging : Pack of 60 Capsules
Prescription Required *
Atazor (Atazanavir) is an antiretroviral medication used to treat human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. It belongs to the class of drugs called protease inhibitors, which block the activity of the protease enzyme in HIV infected cells. By doing so, it prevents the virus from replicating and decreases its overall presence in the body.
Uses:
Atazanavir is used for the treatment of HIV infection in adults and children 3 months of age or older. It is always used in combination with other antiretroviral medications to suppress the virus and prevent disease progression. Atazor can help improve the patient’s immune system, keep their viral load low, and reduce the risk of developing acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) or other HIV-related illnesses.
HOW TO USE:
Atazor should be taken orally, once a day with a meal. The dose of Atazor depends on the patient’s body weight and other medications they are taking. It is important to follow the instructions given by the doctor or pharmacist and to not skip doses. This medication should not be taken with antacids, as they can reduce its effectiveness.
Storage Conditions:
Store Atazor at room temperature (between 20°C- 25°C) in a dry place and keep away from moisture. Keep the medicine out of the reach of children.
Mechanism of Action:
Atazor works by inhibiting the activity of HIV-1 protease, which is necessary to cleave newly synthesized viral proteins into functional parts for the replication cycle of HIV-1 viruses.
Precautions:
It is important to inform the doctor about any allergies or other medical conditions before taking Atazor. This medication may interact with certain other drugs, so it is important to inform the doctor of all medications being taken. Atazor should not be prescribed to patients with severe kidney disease or liver disease.
Contraindications:
Atazor is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to Atazanavir or any of its ingredients. It should not be given to patients already receiving certain medicines, including Cisapride, Lovastatin, Simvastatin, Rifampin, etc.
Drug Interactions:
Atazor may interact with certain other drugs, including Rifabutin, Warfarin, Clarithromycin, or St. John’s wort, which may affect the levels of Atazanavir in the blood and could increase the risk of side effects.
Overdose:
Overdose of Atazanavir may cause serious side effects such as kidney failure, liver problems, and heart rhythm disturbances. In case of overdose, seek immediate medical attention.
Side Effects:
Atazanavir may cause side effects, which can range from mild to life-threatening. Common side effects include dizziness, headache, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Serious side effects include liver problems and an increased risk of bleeding. Patients experiencing any side effects should contact their doctor immediately.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.