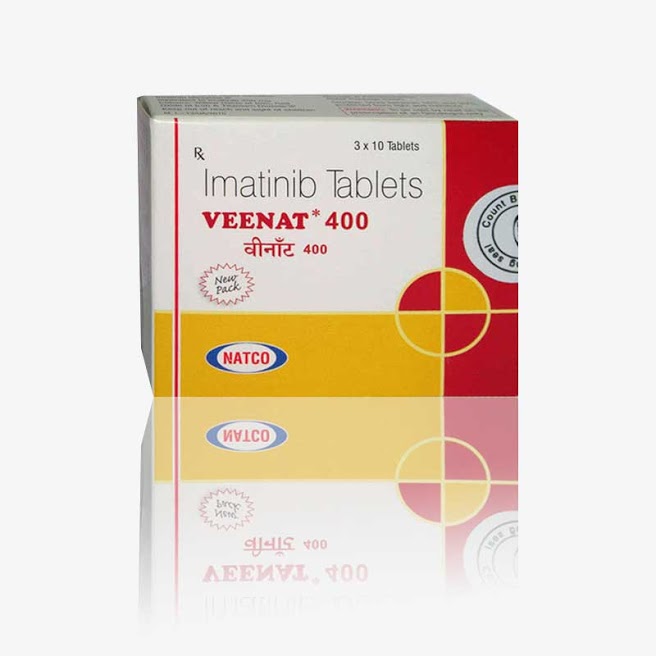
Buy Veenat : Imatinib Mesylate 400 Mg Tablets 30’S Online Natco Pharma
$50.18
Brand Name : Veenat
Composition : Imatinib Mesylate
Manufactured by : Natco Pharma Ltd.
Strength : 400 mg
Form : Tablets
Packing : Pack of 30 Tablets
Prescription Required *
Veenat, also known by its generic name Imatinib Mesylate, is a medication used to treat certain types of cancer, including leukemia and gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs). It is marketed by Natco Pharma Ltd. in the form of 400 mg tablets packed in a pack of 30 tablets. It works by inhibiting certain proteins that are responsible for the growth and spread of cancer cells.
Uses:
– Veenat is used to treat chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
– It is used to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) when other treatments have failed or are not well-tolerated.
– It is also used to treat gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs).
– Veenat may be used for other conditions as determined by a healthcare professional.
How to Use:
– Veenat should be taken as directed by the healthcare professional who prescribed it.
– It is usually taken orally with a full glass of water.
– The tablet should be swallowed whole and not crushed or chewed.
– The dosing schedule and duration of treatment may vary depending on the patient’s condition and response to treatment.
– It is important to follow the dosage instructions and not miss any doses to ensure the effectiveness of treatment.
Storage Conditions:
– Veenat should be stored at room temperature between 15-25°C.
– It should be kept in its original packaging to protect it from light and moisture.
– Keep out of reach of children and pets.
Mechanism of Action:
– Veenat works by inhibiting specific proteins, such as Bcr-Abl and c-Kit, which are responsible for the growth and spread of cancer cells.
– By inhibiting these proteins, Veenat prevents the cancer cells from dividing and multiplying.
– This results in the reduction of the size of tumors and a decrease in the spread of cancer.
Precautions:
– Veenat should not be used in patients who are allergic to it or any of its components.
– It should be used with caution in patients with a history of liver disease, renal impairment, or heart disease.
– It should be used with caution in patients taking other medications that may interact with it.
– Patients should be regularly monitored for signs of liver or kidney damage.
Contraindications:
– Veenat should not be used in patients with severe liver disease.
– It should not be used in pregnant women without consulting a healthcare professional.
– It should not be used in patients taking medications that may interact with it, such as carbamazepine and rifampin.
Drug Interactions:
– Veenat may interact with other medications, such as antacids, calcium channel blockers, and anticoagulants, among others.
– Healthcare professionals should be aware of the potential drug interactions and adjust the dosage accordingly.
Overdose:
– In case of an overdose, seek medical attention immediately.
– Symptoms of an overdose may include stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Side Effects:
– The most common side effects of Veenat include nausea, diarrhea, muscle cramps, and rash.
– Other side effects may include anemia, low platelet count, and liver or kidney damage.
– Patients should report any side effects to their healthcare professional.
Be the first to review “Buy Veenat : Imatinib Mesylate 400 Mg Tablets 30’S Online Natco Pharma” Cancel reply
Related products
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.