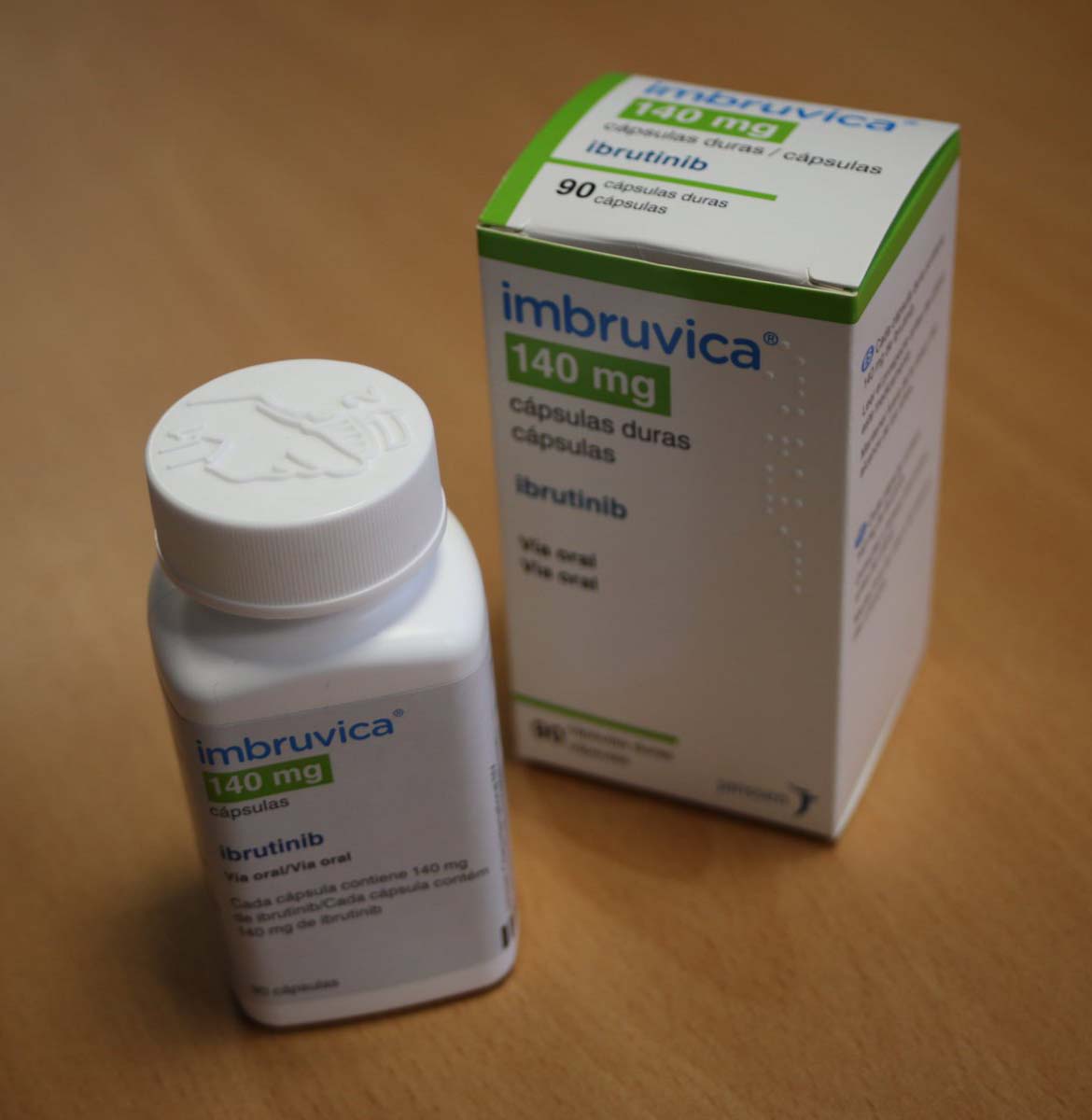
Buy Imbruvica (ibrutinib) 140Mg Capsules Online
$2,870.00
Imbruvica (ibrutinib) is a targeted therapy used to treat various types of blood cancers by inhibiting the protein Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK), which allows for the growth and survival of cancer cells. Imbruvica is a long-term therapy prescribed once daily, and patients may continue treatment as long as they respond well. The capsules should be taken orally and are available in different dosages depending on the type of cancer being treated. Side effects may include nausea and bleeding, and patients should inform their doctor of any other medications they are taking to avoid drug interactions. Imbruvica should not be taken if a patient is allergic to the drug or is pregnant or breastfeeding. Patients should seek the guidance of their healthcare provider before taking Imbruvica.
Introduction
Imbruvica (ibrutinib) is a prescription medication used in the treatment of several types of blood cancers, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM), and marginal zone lymphoma (MZL). The drug works by inhibiting a protein called Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK), which is involved in the growth and survival of cancer cells. Imbruvica is a targeted therapy that selectively targets cancer cells while sparing healthy cells.
Uses
Imbruvica is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of CLL, MCL, WM, and MZL. The drug is indicated for use in patients who have received at least one previous therapy. Imbruvica is intended to be used as a long-term therapy, and patients may continue to receive the drug as long as they are responding to treatment and are able to tolerate the drug.
How It Works
Imbruvica is a BTK inhibitor that binds covalently to the enzyme, blocking its activity. BTK is a key enzyme in the B-cell receptor signaling pathway, which is involved in the growth, survival, and proliferation of cancer cells. By inhibiting BTK, Imbruvica stops the signaling pathway and reduces the survival and proliferation of cancer cells. The drug also has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help control symptoms such as swelling and pain.
Dosing
Imbruvica is taken orally as a capsule and is usually prescribed at a dose of 140 mg once daily for patients with CLL, MCL, or MZL. Patients with WM may receive 420 mg once daily. The drug should be taken at the same time every day with a glass of water. It can be taken with or without food. Patients should not crush, open, or chew the capsules, as this can alter the drug’s release rate and increase the risk of side effects.
Side Effects
Some common side effects of Imbruvica include diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, muscle pain, and upper respiratory tract infections. The drug can also increase the risk of bleeding and bruising, especially in patients taking blood thinners or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Patients should be monitored closely for signs of bleeding, including easy bruising, nosebleeds, bleeding gums, and blood in the urine or stool. Other less common but more serious side effects of Imbruvica include atrial fibrillation, hypertension, and infections such as pneumonia, sepsis, and hepatitis B. Patients should inform their healthcare provider immediately if they experience any unusual symptoms while taking Imbruvica.
Drug Interactions
Imbruvica can interact with other medications, including blood thinners, NSAIDs, and drugs that affect the liver enzymes responsible for metabolizing Imbruvica. Patients should notify their healthcare provider of all medications they are taking, including prescription, over-the-counter, herbal, and vitamin supplements, to avoid potential drug interactions.
Contraindications
Imbruvica is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to the drug or any of its components. The drug should also not be used in patients who are pregnant or breastfeeding, as it may cause harm to the developing fetus or infant.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Imbruvica has been classified as a Pregnancy Category D drug, meaning it may be harmful to the developing fetus. Women of childbearing potential should use effective contraception during treatment and for at least one month after the last dose of Imbruvica. It is also unknown whether Imbruvica is excreted in breast milk, and women should avoid breastfeeding while on this medication.
Conclusion
Imbruvica (ibrutinib) is a targeted therapy used in the treatment of several types of blood cancers, including CLL, MCL, WM, and MZL. The drug works by inhibiting BTK, a key enzyme in the B-cell receptor signaling pathway, which is involved in the growth and survival of cancer cells. Imbruvica is taken orally as a capsule, and the dose will depend on the type of cancer being treated. Side effects of Imbruvica can include diarrhea, fatigue, bleeding, and infections. The drug is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to its components and is not recommended for use in pregnant or breastfeeding women. Patients should discuss the risks and benefits of Imbruvica with their healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Be the first to review “Buy Imbruvica (ibrutinib) 140Mg Capsules Online” Cancel reply
Related products
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.