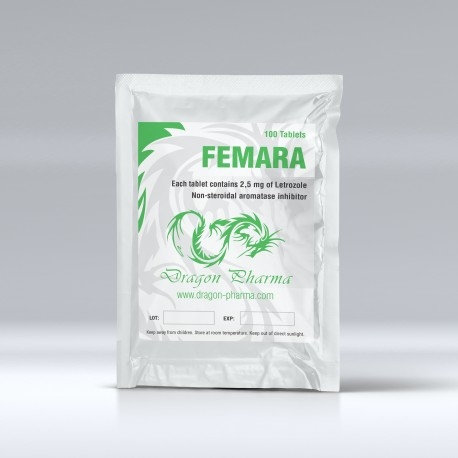
Buy FEMARA Letrozole 100 pills x 2.5 mg Dragon Pharma Online
$50.18
Active Substance: Letrozole
Classification: Non-Steroidal Aromatase Inhibitor
Active Half-Life: 2 Days
Dosage: 0.5 – 2.5 mg/day
Form: 100 pills x 2.5 mg
Manufacturer: Dragon Pharma
Acne: No
Water Retention: No
HBR: No
Hepatoxicity: No
Aromatization: No
- Chemical name: 4-[(4-cyanophenyl)-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl]benzonitrile;
- Formula: C17H11N5
Femara (Letrozole) is a non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor drug used to treat postmenopausal women with hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer. It works by reducing the amount of estrogen in the body, which can slow or stop the growth of some types of breast cancer cells.
Uses:
– Treatment of advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women
– Treatment after surgery for early-stage breast cancer in postmenopausal women
– Treatment of infertility in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
– Off-label use in men with gynecomastia (abnormal breast tissue growth)
How to Use:
– Take Femara as directed by your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
– The usual dose for breast cancer is 2.5 mg/day, but may range from 0.5 to 2.5 mg/day.
– For infertility treatment, the usual dose is 2.5 mg/day on days 3-7 of the menstrual cycle.
– Femara can be taken with or without food, but should be taken at the same time each day.
– Do not crush, chew or break the tablet. Swallow it whole with water.
Storage Conditions:
– Store Femara at room temperature (68-77 degrees F).
– Keep away from light, moisture and heat.
– Keep out of reach of children and pets.
Mechanism of action:
– Femara inhibits the aromatase enzyme, which converts androgens (male hormones) into estrogen (female hormone).
– By reducing the amount of estrogen in the body, Femara can slow or stop the growth of some types of breast cancer cells.
Precautions:
– Femara may cause dizziness or blurred vision. Do not drive or operate machinery until you know how the drug affects you.
– Inform your healthcare provider if you are allergic to letrozole or any other drug.
– Inform your healthcare provider if you have any liver or kidney disease, high cholesterol, or osteoporosis.
– Femara may cause changes in your menstrual cycle. Inform your healthcare provider if you experience irregular periods, vaginal bleeding, or other changes in your menstrual cycle.
Contraindications:
– Do not take Femara if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
– Do not take Femara if you have not reached menopause.
– Inform your healthcare provider if you have a history of blood clots or stroke.
Drug Interactions:
– Femara may interact with some drugs that are metabolized by the liver. Inform your healthcare provider if you are taking any other drugs.
– Femara may reduce the efficacy of tamoxifen (another breast cancer drug).
Overdose:
– If you suspect an overdose of Femara, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
– Symptoms of overdose may include nausea, vomiting, and headache.
Side effects:
– Common side effects of Femara include hot flashes, joint pain, fatigue, muscle pain, and headache.
– Less common side effects include increased risk of fracture, cataracts, and cardiovascular disease.
– Inform your healthcare provider if you experience any unusual symptoms while taking Femara.
Be the first to review “Buy FEMARA Letrozole 100 pills x 2.5 mg Dragon Pharma Online” Cancel reply
Related products
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.