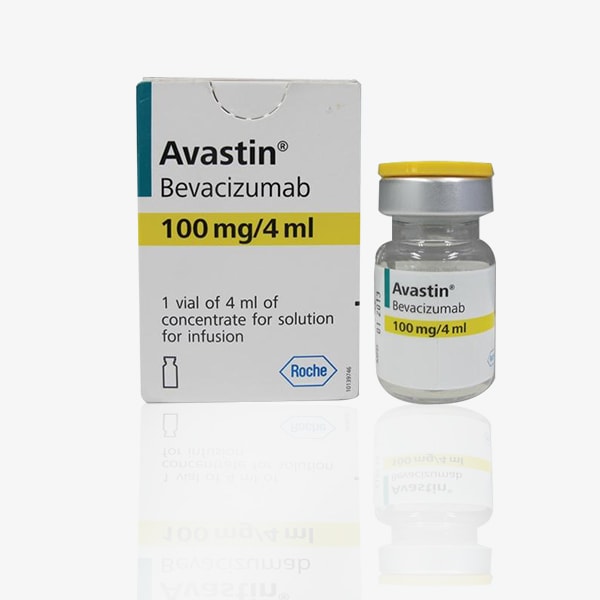
Buy Avastin : Bevacizumab 100 Mg/4 Ml Injection Online
$236.18
Brand Name : Avastin
Composition : Bevacizumab
Manufactured by : Roche Holding AG
Strength : 100 mg/4mL
Form : Injection
Packing : Pack of 1 Vial
Prescription Required:
Description:
Avastin is a medication that contains the active ingredient bevacizumab, which is used to treat different cancers. It is an inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A), a protein that promotes blood vessel growth. By restricting the growth of new blood vessels, Avastin helps slow down the growth and spread of tumors.
Mechanism of Action:
Bevacizumab (Avastin) blocks the VEGF-A protein, which is involved in blood vessel growth. Tumors need blood vessels to grow and spread, and Avastin helps starve them by preventing the formation of new blood vessels. This also helps to cut off the supply of oxygen and nutrients to cancer cells, limiting their growth and survival.
Dosage and Administration:
Avastin is administered as an intravenous (IV) infusion, typically in a hospital or medical facility. The dosage is based on the patient’s weight and medical history, which is determined by a healthcare provider. The medication is usually given every 2 to 3 weeks, depending on the severity of the cancer.
The injection is administered slowly over a period of around 90 minutes, and patients are monitored closely throughout the procedure. The initial dose for adults is 5 mg/kg given every two weeks. Dosages can range from a minimum of 2.5 mg/kg to a maximum of 15 mg/kg per treatment cycle.
Instructions:
Patients should inform their doctor about any previous medical conditions, allergies, or medications they are taking before starting Avastin. Patients should also inform their healthcare provider if they are pregnant or plan to become pregnant as Avastin has adverse effects during pregnancy.
During treatment, patients should avoid any medications or supplements that can increase the risk of bleeding, such as aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Patients should also avoid receiving live vaccines during treatment.
Side Effects:
The most common side effects of Avastin include fatigue, headache, high blood pressure, and nosebleeds. Other potential side effects include abdominal pain, vomiting, loss of appetite, and mouth sores.
More severe side effects include blood clots, bleeding, and stroke. A small number of patients may experience heart failure, gastrointestinal perforation, or kidney problems. Patients undergoing Avastin therapy should report any unusual symptoms to their healthcare provider.
Conclusion:
Avastin is a medication that is effective for treating certain types of cancer. As with any medication, there are potential risks and side effects associated with its use. Patients taking Avastin should be closely monitored by a healthcare provider and should report any unusual symptoms or side effects immediately.
Be the first to review “Buy Avastin : Bevacizumab 100 Mg/4 Ml Injection Online” Cancel reply
Related products
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer
Anti Cancer







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.