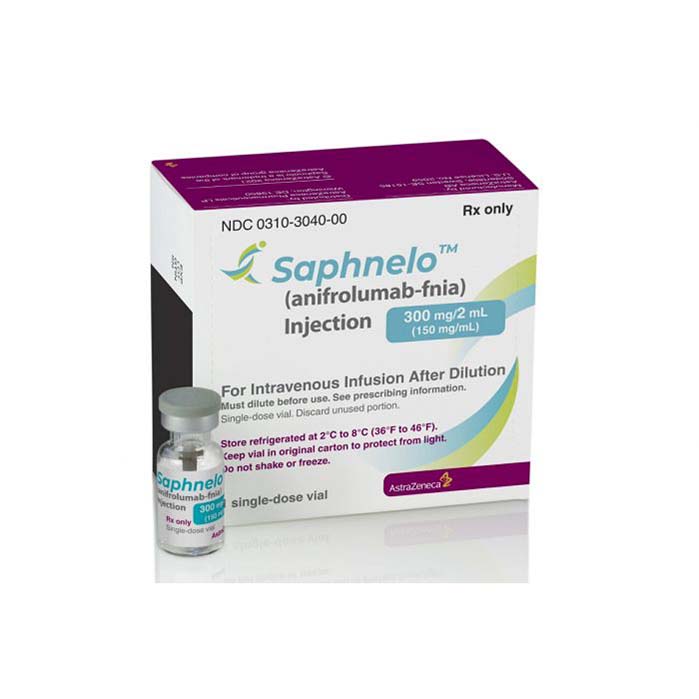
Buy Saphnelo (anifrolumab) Online
$5,560.00
Saphnelo (anifrolumab) is an FDA-approved medication for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in adults. Anifrolumab targets type I interferon receptor, which is overexpressed in many SLE patients, leading to inflammation and organ damage. The medication works by reducing inflammation and disease activity and has been shown to reduce flare rates and corticosteroid use in clinical trials. Anifrolumab is given as an intravenous infusion every four weeks and may have side effects such as nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infections, and infusion reactions. Nonetheless, anifrolumab is a hopeful treatment option for SLE patients who need effective therapies.
Saphnelo (anifrolumab) is a medication approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of adult patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who have had an inadequate response to standard therapy. SLE is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation and damage to multiple organs and tissues, including the skin, joints, kidneys, and central nervous system.
Anifrolumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets the type I interferon receptor, which is overexpressed in many patients with SLE. Type I interferons are cytokines that play a critical role in the pathogenesis of SLE, as they can stimulate proinflammatory immune responses and activate autoimmune cells.
Anifrolumab works by blocking the type I interferon receptor and inhibiting the response to type I interferon, leading to a reduction in inflammation and disease activity in patients with SLE. Clinical trials have shown that treatment with anifrolumab can reduce disease activity, flare rates, and corticosteroid use in patients with SLE.
In a phase III clinical trial called TULIP-2, anifrolumab was compared to a placebo in patients with moderate-to-severe SLE who were receiving standard therapy. The study demonstrated a significantly greater proportion of anifrolumab-treated patients achieving the primary endpoint of a reduction in disease activity at week 52 compared to placebo. Additionally, the study revealed fewer flares and reduced corticosteroid use in patients who received anifrolumab compared to those who received the placebo.
Anifrolumab is given as an intravenous infusion every four weeks. The most common adverse reactions observed in clinical trials include nasopharyngitis (inflammation of the nose and throat), upper respiratory tract infections, infusion reactions, and herpes zoster. Patients with a history of active or chronic infections should be monitored carefully while on anifrolumab.
Anifrolumab represents a valuable addition to the treatment armamentarium for patients with SLE who have had an inadequate response to standard therapy. It specifically targets the type I interferon pathway, which is believed to play a key role in the pathogenesis of SLE. Its efficacy and safety have been demonstrated in clinical trials, providing hope for SLE patients who need effective treatment options.
In conclusion, Saphnelo (anifrolumab) is a medication approved by the FDA for the treatment of adult patients with SLE who have had an inadequate response to standard therapy. It works by blocking the type I interferon receptor, leading to a reduction in inflammation and disease activity in patients with SLE. Clinical trials have demonstrated its efficacy in reducing disease activity, flare rates, and corticosteroid use in patients with SLE. The medication is given as an intravenous infusion every four weeks, and its most common side effects are nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infections, infusion reactions, and herpes zoster. Since it targets the type I interferon pathway, which plays a crucial role in SLE, anifrolumab offers a promising treatment option for SLE patients who require new and effective therapies.
| Package | One vial of 300 mg/2 mL |
|---|
Be the first to review “Buy Saphnelo (anifrolumab) Online” Cancel reply
Related products
Inflammatory Disease
Inflammatory Disease
Inflammatory Disease
Inflammatory Disease
Inflammatory Disease
Inflammatory Disease
Inflammatory Disease
Inflammatory Disease



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.