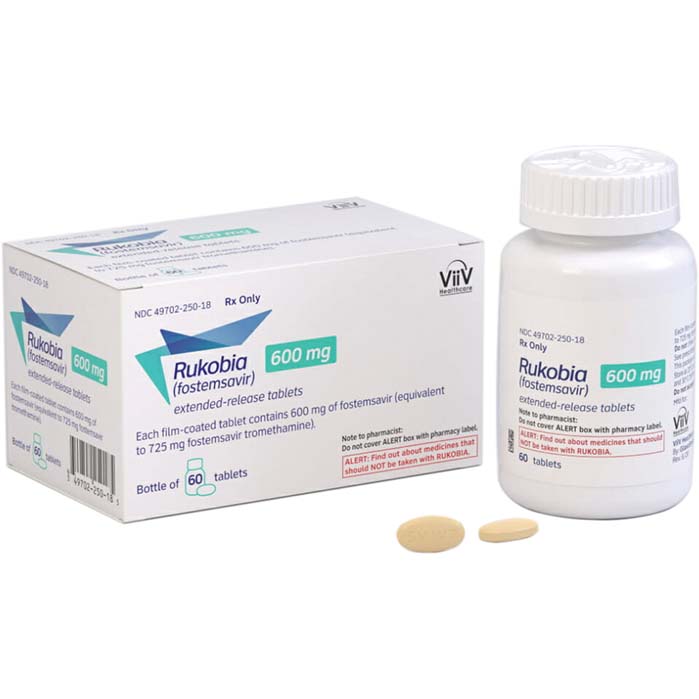
Buy Rukobia (fostemsavir) Online For Sale
DISEASE INDICATIONS: HIV/AIDS
MANUFACTURER: ViiV Healthcare
USAGE: Oral
MEDICINE APPROVED BY: Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
Rukobia (fostemsavir) is a first-in-class attachment inhibitor used to treat HIV-1.
Rukobia (fostemsavir) is a first-in-class attachment inhibitor used for the treatment of HIV-1. It works by targeting the first step of the HIV-1 viral life cycle, which involves the attachment of the virus to the host cell. Rukobia prevents the virus from entering the host cell, thereby curbing its replication.
The medication is specifically indicated for adults who have received prior treatment for HIV-1 and whose infection is not responding to conventional treatments due to resistance or intolerance. It is administered in conjunction with other antiretroviral medications and is taken orally as tablets.
Fostemsavir was granted accelerated approval by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in July 2020, becoming the first attachment inhibitor to be approved for HIV-1 treatment. It is marketed by ViiV Healthcare and is available only through a restricted distribution program due to the potential for adverse reactions.
The recommended dosage of Rukobia is 600mg taken twice daily in conjunction with other antiretroviral medications. The medication has been shown to be effective in clinical trials, inducing viral suppression in a significant proportion of patients with resistant HIV-1 strains.
The safety profile of Rukobia is generally well-tolerated, with the most common side effects being nausea, headache, fatigue, and diarrhea. The medication can also cause severe allergic reactions, liver damage, and other adverse effects, requiring close monitoring during treatment.
In conclusion, Rukobia (fostemsavir) is a first-in-class attachment inhibitor used for the treatment of HIV-1 in adults who have developed resistance to conventional antiretroviral therapies or who are intolerant to them. The medication is taken orally and is used in conjunction with other antiretroviral medications. Its approval by the FDA marks a significant milestone in the treatment of HIV-1, offering new hope for patients who have previously experienced treatment failure. The medication has a generally well-tolerated safety profile and has shown promising results in clinical trials, although it can cause severe adverse reactions, requiring close monitoring during treatment.
| Package | 60 tablets of 600 mg |
|---|
Be the first to review “Buy Rukobia (fostemsavir) Online For Sale” Cancel reply
Related products
Infectiology
Infectiology
Infectiology
Dermatology
Infectiology





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.