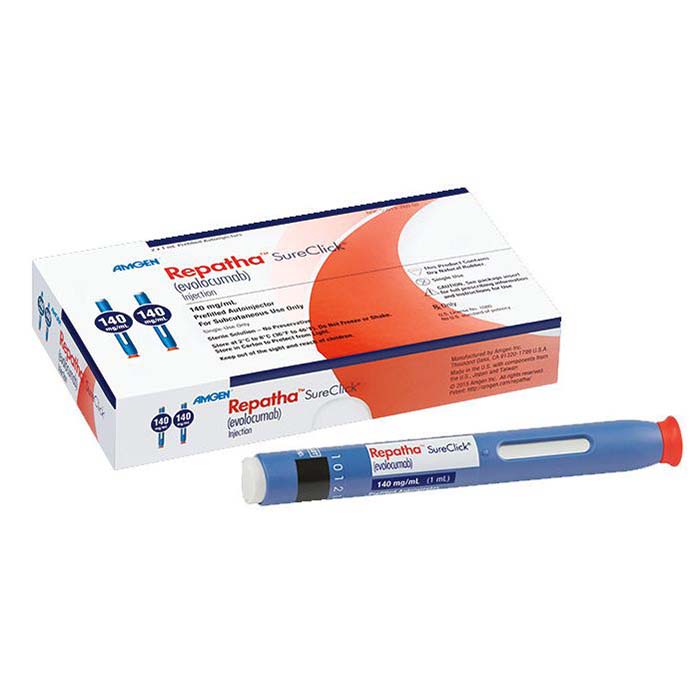
Buy Repatha SureClick (evolocumab) Online For Sale
$588.00
DISEASE INDICATIONS: Risk of cardiovascular events, Hypercholesterolemia
MANUFACTURER: Amgen Inc.
USAGE: Subcutaneous
MEDICINE APPROVED BY:
European Medical Agency (EMA)
Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
Health Canada
Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA)
Repatha (evolocumab) is a medication used to lower LDL cholesterol levels. It works by binding to PCSK9 which increases the number of LDL receptors on the liver resulting in a decrease in LDL cholesterol levels. It was approved by the FDA in 2015 and is usually used for patients in high cardiovascular risk or familial hypercholesterolemia.
Repatha (evolocumab) is a prescription medication used to lower low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels in adults with certain types of high cholesterol. It was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on August 27, 2015, and is manufactured by Amgen Inc.
What is high cholesterol?
High cholesterol is a condition in which there is an excessive amount of cholesterol in the blood. Cholesterol is a fatty substance that is essential for many bodily functions, but too much LDL cholesterol (the “bad cholesterol”) in the blood can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
How does Repatha work?
Repatha is a human monoclonal antibody that works by binding to a protein called proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9). PCSK9 is a protein that regulates the amount of LDL cholesterol in the blood by reducing the number of LDL receptors on the liver, which are responsible for removing LDL cholesterol from the blood. By binding to PCSK9, Repatha increases the number of LDL receptors on the liver, which results in a decrease in LDL cholesterol levels.
Clinical trials for Repatha
The approval of Repatha by the FDA was based on several clinical trials, including the FOURIER trial, which enrolled 27,564 patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and LDL cholesterol levels above 70 mg/dL who were already receiving statin therapy. Patients were randomized to receive either Repatha or placebo, in addition to standard therapy. The study found that Repatha reduced the risk of cardiovascular events (such as heart attack, stroke, and angina requiring hospitalization) by 15% compared to placebo. Additionally, Repatha was well-tolerated, with similar rates of adverse events in both treatment groups.
Side effects of Repatha
The most common side effects of Repatha include injection site reactions such as pain, redness, and swelling. Other side effects may include flu-like symptoms, such as fever, chills, and muscle pain. In rare cases, Repatha may lead to serious allergic reactions and liver problems. Patients should contact their healthcare provider immediately if they experience symptoms such as difficulty breathing, rash, or swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Repatha and other cholesterol medications
Repatha is not intended to replace other cholesterol-lowering medications, such as statins or ezetimibe. Instead, Repatha is a new option for patients who have high LDL cholesterol levels despite being treated with these medications. Repatha is usually only used in patients who have high cardiovascular risk or familial hypercholesterolemia (a genetic condition that causes high cholesterol levels).
Conclusion
Repatha (evolocumab) is a medication used to lower LDL cholesterol levels in patients with high cholesterol. It works by binding to a protein called PCSK9, which increases the number of LDL receptors on the liver and results in a decrease in LDL cholesterol levels. The FDA approved it in 2015, and clinical trials have shown that it can reduce the risk of cardiovascular events in patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and high LDL cholesterol levels. Repatha is usually used in patients who have high cardiovascular risk or familial hypercholesterolemia, and it is not intended to replace other cholesterol-lowering medications. Patients should consult their healthcare provider regarding the use of Repatha.
| Package | Two 140 mg/mL single-use prefilled SureClick® autoinjector, Six 140 mg/mL single-use prefilled SureClick® autoinjector, One 420 mg/3.5 mL single-use Pushtronex® system (on-body infusor with prefilled cartridge), Three 420 mg/3.5 mL single-use Pushtronex® system (on-body infusor with prefilled cartridge) |
|---|
3 reviews for Buy Repatha SureClick (evolocumab) Online For Sale
Add a review Cancel reply
Related products
Heart Condition
Heart Condition
Heart Condition
Heart Condition
Heart Condition
Heart Condition
Heart Condition




Emily S –
I have familial hypercholesterolemia, and Repatha SureClick has been vital in controlling my cholesterol levels. The convenience of the SureClick device means I can manage my treatment at home confidently. My recent tests show excellent LDL reductions. I feel empowered and grateful for this medication.
David K –
I was nervous about injectable medications, but Repatha SureClick’s auto-injector is so easy and almost painless. My cardiologist prescribed it after my statins weren’t enough, and I’ve seen great results. My cholesterol is down, and I haven’t experienced side effects. Five stars for both effectiveness and convenience!
Angela M –
After struggling with high LDL cholesterol for years despite lifestyle changes and other medications, Repatha SureClick has been a game changer. The injection is simple to use, and my LDL levels dropped significantly within a few weeks. I feel much more confident about my heart health now. Highly recommend this to anyone needing extra help!